Import and Export Variables Data
Save imported variables as
Microsoft®
Excel®
spreadsheets (.xls) or comma-separated values (.csv).- Export variables to manage simple and complex variables data including adding, removing, and modifying variables.
- Import variables data files into controllers and programs in the same project or in other projects.TIP:
- AADvance-Trusted SIS Workstation software®uses the default values for missing data when importing a variables data file missing any columns.
- Make sure imported variables match their corresponding definitions in the project when importing variables.
Specify a location to save exported files when exporting variables. Export an empty file as a template to develop the contents of variables data files (*.xls or *.csv) in a respective editor like
Microsoft
Excel
or Notepad.A variables data file includes a header row, a mapping row, a version number, and the variables data. The header row displays the names of the data columns. The column names of the header row are the various variable properties. The mapping row displays the internal names of data columns in brackets used for processing. An automatically generated version number indicates the version of the import/export feature. The individual variable data is placed in the respective columns.
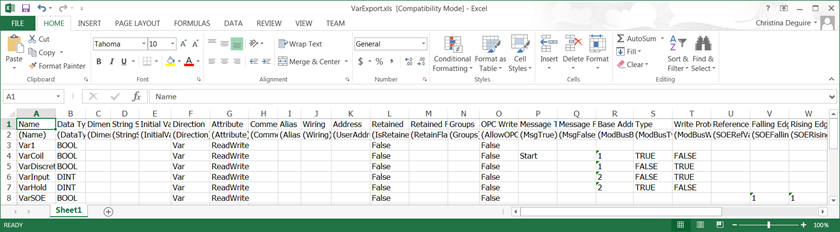
This table shows the syntax used in the variables data files for the variable properties and the associated internal names:
Variable Property | Internal Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name | (Name) | Name of the variable. Variable name are limited to 128 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore character followed by letters, digits, and single underscore characters. The last character for a variable name must be a letter or digit; variable names cannot end with an underscore character. Names cannot be reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays). Names must be unique. |
Data Type | (DataType) | Data type of the variable |
Dimension | (Dimension) | Number of elements defined for an array |
String Size | (StringSize) | The maximum character length for string-type variables. |
Initial Value | (InitialValue) | Value held by a variable when the virtual machine starts executing the controller |
Direction | (Direction) | For the local variables of a program organization unit (POU), indicates whether the variable is internal, an input, or an output. For controller variables, indicates whether the variable is internal, an input, an output, a system variable, or an I/O channel. |
Attribute | (Attribute) | Read and write access rights |
Comment | (Comment) | User-defined free-format text for variables and array elements. Each array element of the same type can have a different comment. |
Alias | (Alias) | Any name |
Wiring | (Wiring) | The I/O channel wired to the variable During variable import, the raw and engineering values of analog I/O channels reset: When imported variables are not wired, the raw values are: 0 for low, and 1 for high. The engineering values are: 0 for low, and 1 for high. When imported variables are wired, the raw values are: 1024 for low, and 5120 for high. The engineering values are: 0 for low, and 100 for high. |
Address | (UserAddress) | User-defined address of the variable |
Retained | (IsRetained) | The virtual machine saves the value of the variable at each cycle. Limitations:
|
Retained Flags | (RetainFlags) | Enables retaining specific elements of a variable and indicates whether to use the initial value of a variable or the value previously retained on the target. |
Groups | (Groups) | Variable group containing the variables listed in alphabetical order |
OPC Write | (AllowOPCWrite) | An external client can write to the variable |
Message True | (MsgTrue) | Message defined for the TRUE value message |
Message False | (MsgFalse) | Message defined for the FALSE value message |
Base Address | (ModBusBaseAddress) | For Modbus communications, the base address of the variable |
Type | (ModBusType) | For Modbus communications, indicates one of these variable types:
|
Write Protected | (ModBusWriteProtected) | For Modbus Communications for Coils and Holding Registers, indicates whether data can be copied from the Modbus master to the slave device. |
Reference Variable | (SOERefVar) | For the SOE service, the referenced variable of any elementary data type. |
Falling Edge Level | (SOEFallingLevel) | Te SOE service detects a fall from TRUE to FALSE. |
Rising Edge Level | (SOERisingLevel) | The SOE service detects a rise from FALSE to TRUE. |
Filter Time | (SOEFilterTime) | For the SOE service, the minimum time lapse between two events. |
CIP Kind | (CIPKind) | For CIP communications, indicates whether the variable is a producer or consumer. |
Producer Name | (CIPProducerName) | When the CIP variable is a consumer, indicates the CIP producer from which the consumer receives data. |
Path To Producer | (CIPCPathToProducer) | When the CIP variable is a consumer, indicates the path to the producer. |
Consumer Remote Tag | (CIPRemoteTag) | When the CIP variable is a consumer, indicates the remote tag name of the producer variable communicating with the consumer variable. |
RPI (ms) | (CIPCRPI) | When the CIP variable is a consumer, indicates the frequency in milliseconds that the remote controller offers the variable to the AADvance controller. |
Producer Remote Tag | (CIPPRemoteTag) | When the CIP variable is a producer, indicates the remote tag name of the consumer variable communicating with the producer variable. |
Max Number of Connections | (CIPPMaxConnections) | When the CIP variable is a producer, the maximum number of simultaneous consumer variables. |
To Controller | (SNCPToController) | For the SNCP producer binding variable, the corresponding controller name for each consumer variable. For multiple consumer variables, controller names are separated by a comma. For example: Controller2,Controller2,Controller3 . |
From Controller | (SNCPFromController) | For the SNCP consumer binding variable, the name of the controller producing the variable binding group. |
From Symbol | (SNCPFromSymbol) | For the SNCP consumer binding variable, the name of the producer variable. |
Error Value | (SNCPErrorValue) | For the SNCP consumer binding variable, the value defined for the error behavior. When no value is specified for the error behavior, the binding uses the last value. |
Update Value | (SNCPUpdateValue) | For the SNCP consumer binding variable, the value defined for the update behavior. When no value is specified for the update behavior, the binding uses the last value. |
A progress bar shows advancement of import and export operations. Use the progress bar to cancel import and export operations.
- For import operations, the process stops after importing the last variable in progress.
- For export operations, the process does not produce an exported variables file.TaskProcedureImport variables
- In theApplication View, right-click the destination receiving theLocal VariablesorController Variables, and then clickImport Variables....
- From theImport Variablesdialog box, select the file type containing the variables, locate the file, and then clickOpen.
Export variables- In theApplication View, right-click theLocal VariablesorController Variablescontaining the variables to export, and then clickExport Variables....
- From theExport Variablesdialog box, specify a name and locate the destination in which to store the file containing the exported variables, select the file type and then clickSave.
Provide Feedback
