Forcing the Values of Variables
While connected or simulating, force or override the values of variables. These variables can be user-defined or directly represented. The behavior of a variable is defined by its logical value, physical value, lock state, and direction. When forcing the values of variables, the value to overwrite depends on the direction of the variable. Force the values of variables from the
Dictionary
, language containers, and the Watch
window.Locking and unlocking operates only on elementary data types for variables, array elements, and structure elements that are wired.
For locked variables, the values displayed in the
Logical Value
and Physical Value
columns differ depending on their direction:Input Variable (Read) Behavior
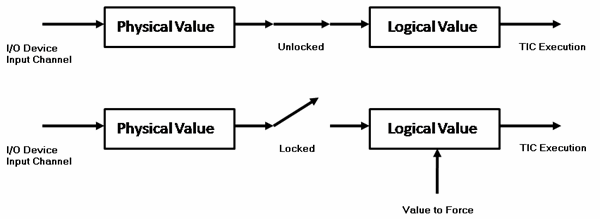
Example: To force the temperature reading from a sensor.
Output Variable (Write) Behavior
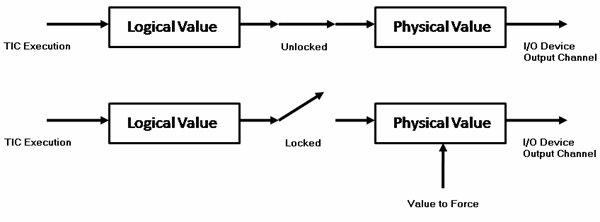
Example: To force the closing of an actuator valve.
TIP:
When you force variable values, the computer running
AADvance-Trusted SIS Workstation software
or AADvance Standalone OPC server sends an IXL write message to
the controller. If the IXL write message is processed right after
Execute target
independent code (TIC)
in the application execution loop (step 4 in Execution Rules), the forced value is used for the producer
binding, wired output, or retained variable. If the IXL write message is processed
right after
Save retain variables
in the current application execution loop (step 8
in Execution Rules), the step Execute target
independent code (TIC)
in the next application execution loop may overwrite the
forced value with a different value for the producer binding, wired output, or retained
variable. To help achieve deterministic behavior, avoid forcing an:
- internal variable that is bound as a producer or retained (internal variables cannot be locked)
- unlocked output variable
To force the values of variables
- From theDictionaryinstance, locate the required variable.
- Write the required value in the respective value column:
- For an input variable, write the value in theLogical Valuecolumn.
- For an output variable, write the value in thePhysical Valuecolumn if the variable is locked and write the value in theLogical Valuecolumn if the variable is unlocked.
Provide Feedback
