Creating Links between Controllers
Links between controllers enable the transfer of values between producer and consumer variables defined in bindings. Before defining variable bindings, create links between controllers with producer variables and consumer variables to use in these bindings.
To use bindings, define at least one Ethernet port to be used by SNCP bindings. When multiple ports are defined, each IP address is pinged to locate accessible links. Communication occurs on the first Ethernet port (slice) selected in the list of ports; the other addresses continue to be pinged. If a timeout occurs on the active link, communications switch to another IP address. To use bindings, configure the SNCP link properties.
TIP:
To correct the port configuration when reopening a
project after changing the port selection:
- Export the variables used in bindings between both controllers.
- Delete the incorrect binding link and save changes.
- Recreate the binding link and save changes.
- Import the exported variables.
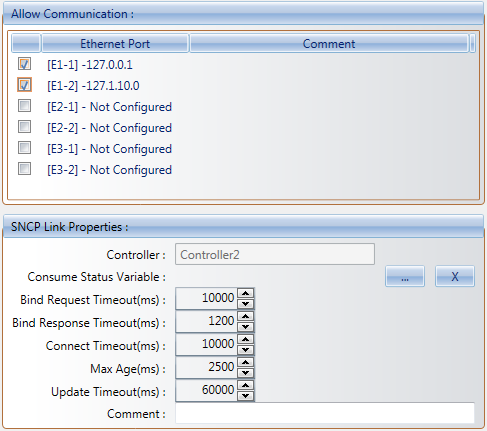
Binding contains these SNCP link properties:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Consume Status Variable | The wired variable used to report the health status of the link. The data type of the variable must be DINT. A healthy binding link returns a value of 0, while a link containing a fault returns a non-zero value.
TIP:
To obtain the correct status, ensure the first mapped variable in
the Bindings list does not use the LINT, ULINT, LWORD, or LREAL data
type.
|
Bind Request Timeout | The time period the producer waits to receive a binding data request from the consumer, in milliseconds. In the event of a timeout, the consumer is disconnected. Subsequent requests from the consumer are ignored until the consumer establishes a new connection.
TIP:
The network binding parameters, for example
timeout values, of the consumer are found in the producing controller.
The
network binding parameters, for example timeout values, of the consumer are
found in the producing controller. Possible values range from 0 to 65535 milliseconds. The default value is 10000 milliseconds. |
Bind Response Timeout | The time period during which the consumer awaits binding values from the producer, in milliseconds. In the event of a timeout, the consumer can send another request (dependent on the value of Max Age) or disconnects from the producer. The number of requests sent is calculated as: Max Age/Bind Response Timeout Once disconnected, the consumer attempts to reestablish the connection by sending a Connect request at Connect Timeout intervals.Possible values range from 0 to 65535 milliseconds. The default value is 1200 milliseconds. |
Connect Timeout | The time period during which a consumer awaits a connection response from a producer, in milliseconds. In the event of a timeout, the consumer sends another Connect request. The consumer continues to send requests until a connection is established. Possible values range from 0 to 65535 milliseconds. The default value is 10000 milliseconds. |
Max Age | The total time, in milliseconds, during which the consumer awaits a valid response from the producer before considering the physical network unhealthy. Stale, corrupt, and out of sequence responses are considered invalid. Continuing to receive these types of responses can indicate underlying network issues, demonstrated by the unhealthy network status. The unhealthy status is reported by the KvbConsNetStatus and KvbProdNetStatus function blocks. The number of requests is calculated as: Max Age/Bind Response Timeout The Max Age is also used to verify the age of the binding response received by the consumer. If a response contains data older than Max Age , the response is discarded. Discrepancies may occur when a response is delayed due to network issues.Possible values range from 0 to 65535 milliseconds. The default value is 2500 milliseconds. |
Update Timeout | The timeout period during which a consumer and producer must reconnect after an update has modified the binding information, in milliseconds.
IMPORTANT:
Perform updates as quickly as
possible to avoid timeouts.
During the Update Timeout period, the configured consume status variable continues to indicate a healthy status even though no connection exists between the consumer and producer. In the event of a timeout, the consume status variable becomes unhealthy.Possible values range from 0 to 65535 milliseconds. The default value is 60000 milliseconds. |
Comment | Plain text |
IMPORTANT:
Linked controllers must have the same SNCP Link
Properties.
Timeout Example
This example displays the timeout behavior when
Max Age
is set to 2500 ms and Bind Response Timeout
is set to 1000 ms: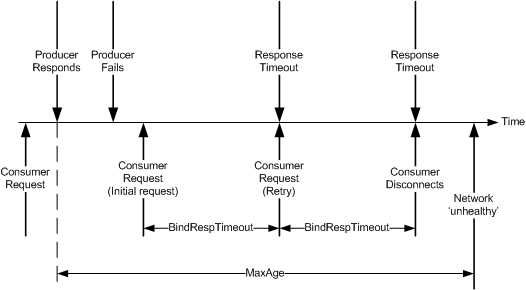
To create a link between controllers
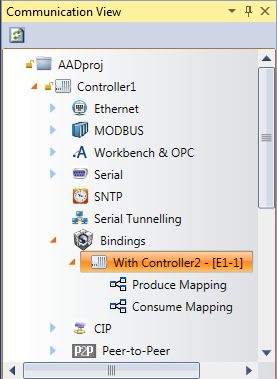
- In theCommunication View, expand the required controller to link, then right-clickBindings, point toAdd Controller Link, and then click the controller with which to link.
- Double-click theBindingslink.
 TheCommunicationproperty page is displayed with theAllow CommunicationandSNCP Link Propertiessections.
TheCommunicationproperty page is displayed with theAllow CommunicationandSNCP Link Propertiessections. - From theCommunicationproperty page, in theAllow Communicationsection, select the required Ethernet ports. The available Ethernet ports are those defined for the individual controllers.
- In the SNCP Link Properties section, enter the required values for the following properties:
- Bind Request Timeout (ms)
- Bind Response Timeout (ms)
- Connect Timeout (ms)
- Max Age (ms)
- Update Timeout (ms)
- If required, click
 to wire a Consume Status Variable.The VariableSelectoris displayed.
to wire a Consume Status Variable.The VariableSelectoris displayed. - In theVariable Selector, select the required variable of type DINT, and then clickOK.
- (optional) To delete a link between controllers, do the following:
- In theCommunication View, expand the required controller, and then expandBindings.
- Right-click the controller link to remove, and then clickDelete.
Provide Feedback
