Import and Export Variables Data
Imported variables are saved as
Microsoft®
Excel®
spreadsheets (.xls) or comma-separated values (.csv). Exporting variables enables managing variables data including adding, removing, and modifying variables. Import variables data files into other devices and programs in the same project or in other projects.The .csv file must be saved with the UTF-8 encoding setting.
TIP:
When importing a variables data file missing any
columns, the
AADvance-Trusted SIS Workstation software®
uses the default values for the missing
data.When exporting variables, specify the location in which to save the exported files. To develop the contents of variables data files (*.xls or *.csv) in a respective editor, for instance,
Microsoft
Excel
or Notepad, export an empty file serving as a template.A variables data file includes a header row, a mapping row, a version number, and the variables data. The header row displays the names of the data columns. The column names of the header row are the various variable properties. The mapping row displays the internal names of data columns in brackets used for processing. An automatically generated version number indicates the version of the import/export feature. The individual variable data is placed in the respective columns.
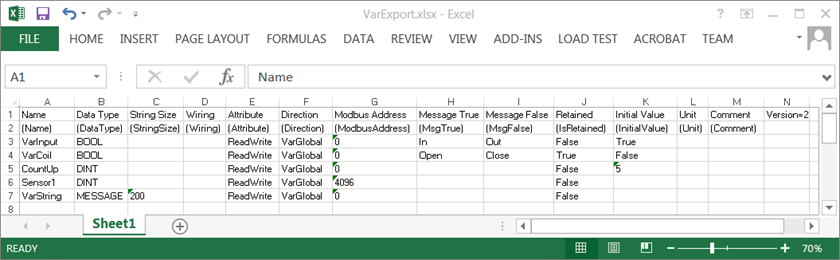
This table indicates the syntax used in the variables data files for the variable properties and the associated internal names:
Variable Property | Internal Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name | (Name) | Name of the variable. Variable names are limited to 32 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore character followed by letters, digits, and single underscore characters. Names cannot be reserved words, defined words, or data types. Names must be unique for the same type of elements within a scope. |
Data Type | (DataType) | Data type of the variable |
String Size | (StringSize) | The maximum character length for string-type (MESSAGE) variables. The string length is limited to 240 characters. |
Wiring | (Wiring) | Indicates the I/O channel wired to the variable |
Attribute | (Attribute) | Read and write access rights |
Direction | (Direction) | For the local variables of a program, indicates the variable is internal. For the local variables of a function or function block, indicates whether the variable is internal, an input, or an output. For the global variables of a device, indicates the variable is internal, for use with I/O wiring, or defined for an I/O channel. |
Modbus Address | (ModbusAddress) | Modbus address of the variable |
Message True | (MsgTrue) | User-defined text that is used by the SOE Collector in the Trusted Sequence of Events and Process Historian Package when the value of a Boolean variable data type is TRUE.Excluding , % “ and without leading and trailing spaces. |
Message False | (MsgFalse) | User-defined text that is used by the SOE Collector in the Trusted Sequence of Events and Process Historian Package when the value of a Boolean variable data type is FALSE.Excluding , % “ and without leading and trailing spaces. |
Retained | (IsRetained) | Indicates whether the virtual machine saves the value of the variable at each cycle |
Initial Value | (InitialValue) | Value held by a variable when the virtual machine starts executing the application |
Unit | (Unit) | A string identifying the physical unit of measure |
Comment | (Comment) | Plain text |
A progress bar indicates the advancement of import and export operations. The progress bar enables canceling import and export operations. For import operations, the process stops after importing the last variable in progress. For export operations, the process does not produce an exported variables file.
Task | Procedure |
|---|---|
Import variables |
|
Export variables |
|
Provide Feedback
