SOCKET_READ
The SOCKET_READ instruction reads data on a socket and returns the specified number of bytes. For Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), returns when any data is received, up to the requested number of bytes. For User Datagram Protocol (UDP), completes when a datagram is available.
Operation details:
The following SOCKET_READ behavior might impact existing communications, including non-socket communication:
- If the SOCKET_READ operation is not executed in sync with the remote device then, the controller holds the remote device receive packet until one of the following occurs:
- SOCKET_READ is executed.
- Socket Timeout expires.
- RST is received from a remote device.
- SOCKET_DELETE or SOCKET_DELETEALL is executed.
- A Run Mode Change is performed, which deletes all created Socket instances.
- Controller changes from run mode to program mode, which deletes all created Socket instances.
- Controller changes from run mode to program mode, which clears socket Diagnostic counter information and individual Socket counter information.
- If the Length or Offset parameter value is changed while the SOCKET_READ operation is ongoing (BUSY = True), an error occurs and the receive packet is discarded.
- The SOCKET_READ instruction might return fewer bytes than were requested. RxLength contains the number of bytes of data received. Write programs to check RxLength and then issue additional read requests to receive an entire application message.
- In Run Mode Change mode, changing a SOCKET_READ input while operating in the BUSY state results in an error and the received packet is discarded.
- Outputs update synchronously from the program scan.
Languages supported: Function block diagram, ladder diagram, structured text.
This instruction applies to the L20E, L50E, and L70E controllers.
SOCKET_READ
Parameter | Parameter Type | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Execute | Input | BOOL | Instruction enable.
|
Instance | Input | UDINT | Copy from the returned Socket Handler from a SOCKET_CREATE or SOCKET_ACCEPT instruction.
|
Timeout | Input | UDINT | Timeout for SOCKET_READ. The instruction block returns an Error if the timeout value is less than the minimum value. Timeout range: 1000-86400000 milliseconds. Set Timeout to 0 to use the default value 10000 (10 Second). |
Length | Input | UINT | Defines the number of bytes to read. Check RxLength for the actual number of bytes read. SOCKET_READ can return fewer bytes than requested. Supports up to 256 bytes. |
Offset | Input | UNIT | Offset into array of Data. Start reading data read from this location. |
Data | Output | USINT[1..1] | An Array used to store the data read from SOCKET_READ.
Output is updated synchronously from the program scan. |
Done | Output | BOOL | Indicates when operation is complete.
Output is updated synchronously from the program scan. |
Busy | Output | BOOL |
Output is updated synchronously from the program scan. |
Error | Output | BOOL | Indicates an error occurred.
Output is updated synchronously from the program scan. |
Status | Output | SOCK_STATUS | Status is defined using the SOCK_STATUS data type, which contains ErrorID, SubErrorID, and StatusBits information. Output is updated synchronously from the program scan. |
RxLength | Output | UNIT | Contains the number of data bytes received. |
UDPAddr | Output | The address of the device sending User Datagram Protocol (UDP) data. Example defines a UDPAddr of 192.168.2.100 and Port 12000: UDPAddr.IPAddress[0]=192 UDPAddr.IPAddress[1]=168 UDPAddr.IPAddress[2]=2 UDPAddr.IPAddress[3]=100 UDPAddr.Port = 12000 For Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), this structure is not used and contain all zeros. The TCP connection conveys the remote address information. |
SOCKET_READ examples
SOCKET_READ function block diagram example
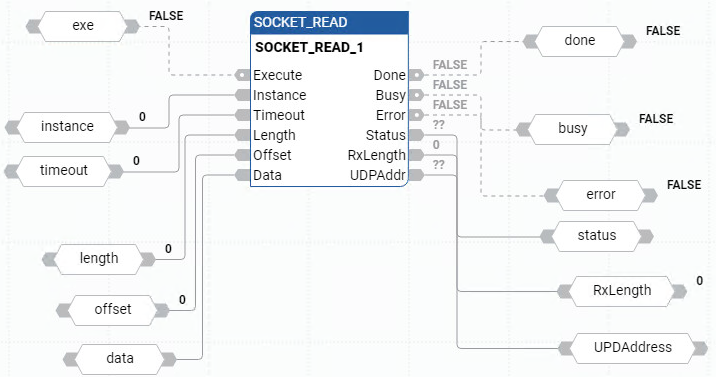
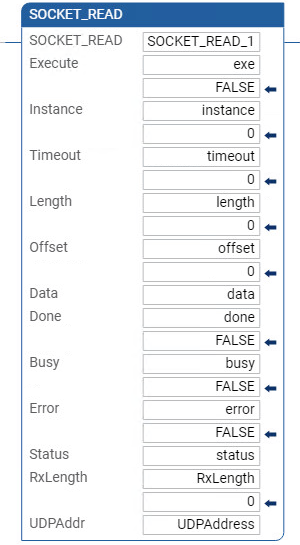
SOCKET_READ ladder diagram example
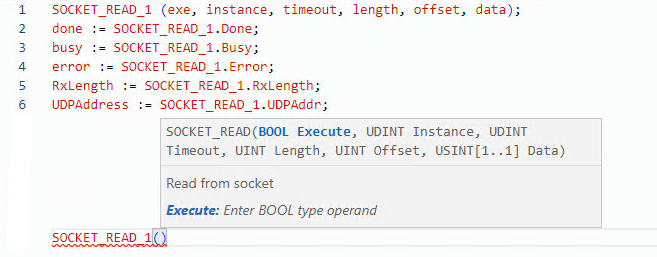
SOCKET_READ structured text example
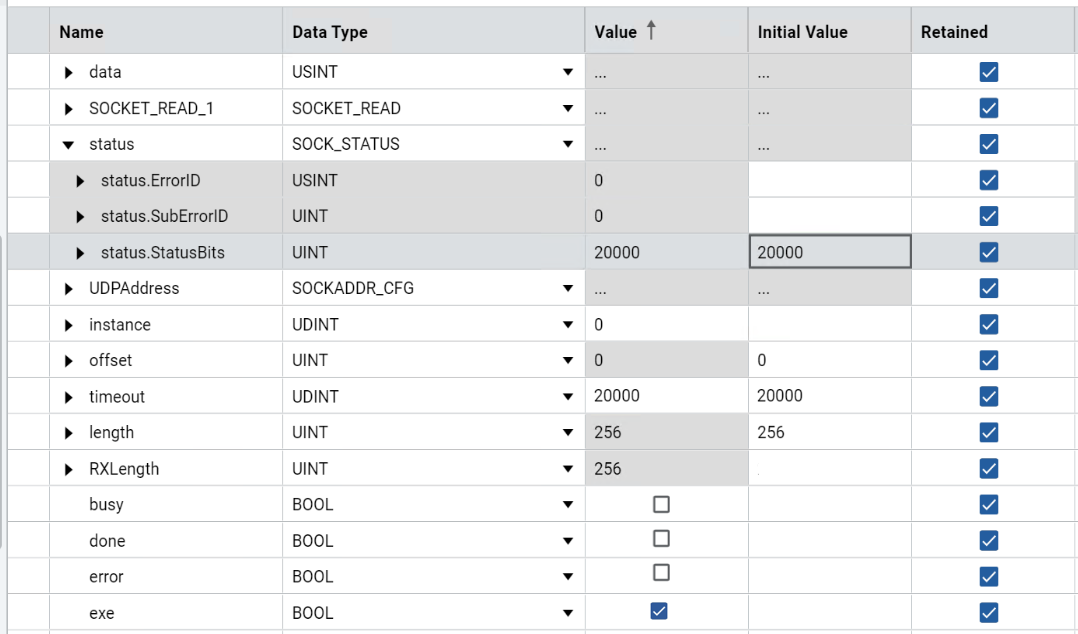
Results - TCP
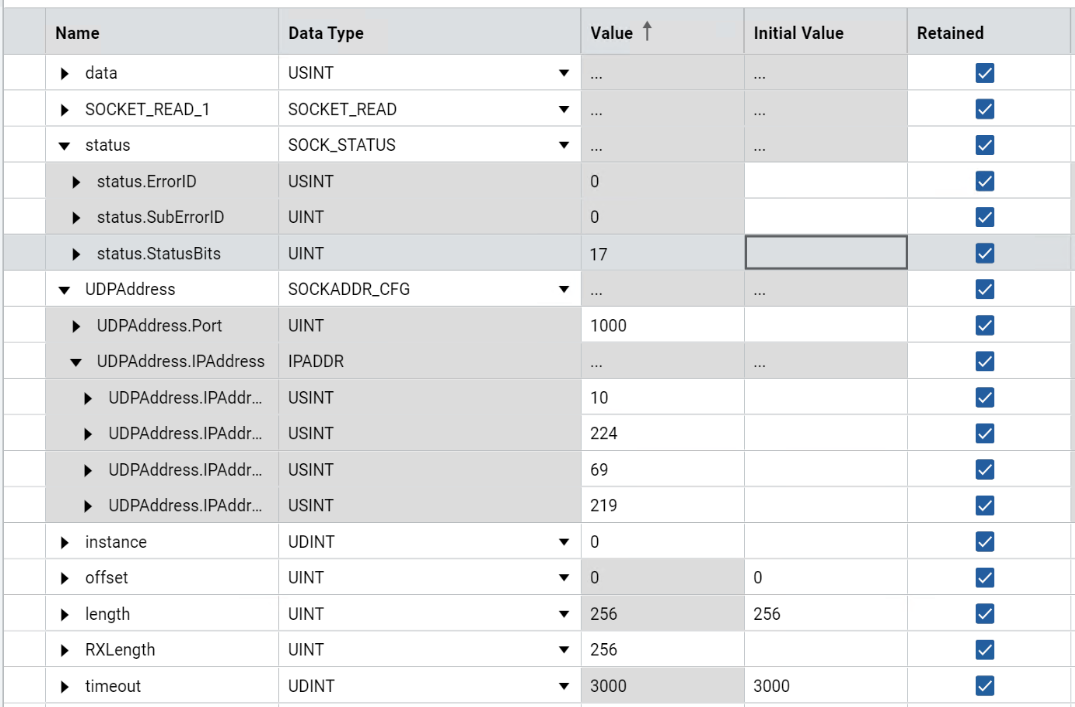
Results - UDP
Provide Feedback
