Ready for the Ford FMEA Software Requirement?
Tier 1 automotive suppliers have a critical choice to make when it comes to quality management. Plex Quality Management System (QMS) helps manufacturers like you take the guesswork out of quality management by ensuring predictability and repeatability. Discover the difference that a digital quality management solution can make!
The automotive space is exciting, but constant changes in technology and disruption can be challenging.
It doesn't matter if you're a mature automaker, startup electric vehicle (EV) company, tire producer, battery producer, or tier supplier. The growth of EVs, new battery technology, increased customization, and the future of ride-sharing impact all of us – consumers, manufacturers, and innovators.
So, call the new era of automotive manufacturing what you will. Smart manufacturing. E-mobility. Industry 4.0 Automotive. The bottom line is this: A fast start and rethinking how things are made will be vital to remaining relevant. To get to market first, you need a partner, a catalyst, to help you succeed.
Rockwell Automation has built the tools you need to manage that change and drive it. Our singular focus on automation, combined with our deep automotive manufacturing experience, means that we understand your world and how to improve on it. We bring a passion for connecting people's imaginations with machines' potential to make your plant work smarter today and tomorrow.
Solutions for Automotive and Tire
Accelerate Operations and Stay Ahead of the Competition with Automated Automotive Solutions
Increase Efficiency
Harness the power of disruptive technologies to improve decision-making in your plant.

Optimize Production
Meet consumer demands with a connected, information-driven approach.

Accelerate Time to Market
Develop a scalable production strategy with proven approaches.
Automotive Automation in Manufacturing: What You Need to Know
What is Automotive Automation?
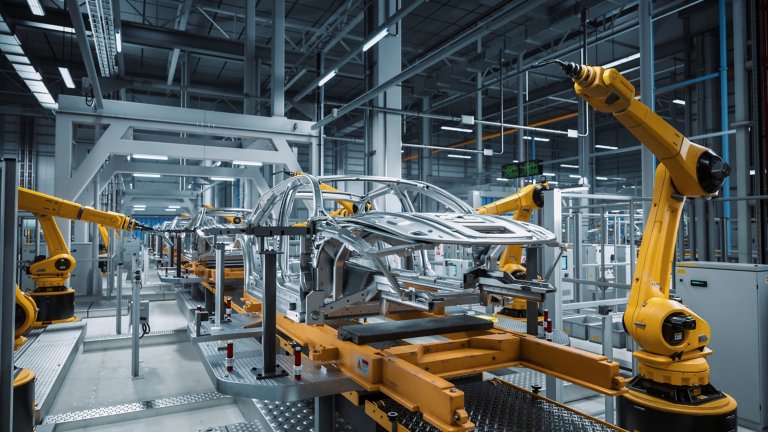
Automotive automation refers to the use of advanced manufacturing, or ‘smart,’ technology in automotive manufacturing. Through the use of robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), automotive manufacturers can enhance nearly every stage of the manufacturing process, from material supply to assembly and delivery.
Automotive automation enables manufacturers to save time, increase production capacity, and protect employees from dangerous conditions and repetitive labor, all without sacrificing quality assurance.
What is Automotive Manufacturing?
Automotive manufacturing refers to the process of designing, developing, and producing automobiles, trucks, and other motor vehicles, along with the various parts and components that make them up.
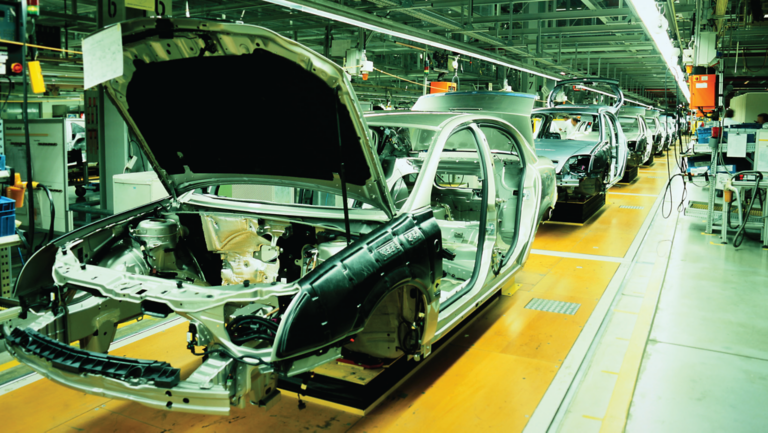
Automotive manufacturing is a complex process that involves a number of key steps, from vehicle and parts design to assembly and testing, among others. In order to perform these key steps, automotive manufacturing makes use of many specialized pieces of equipment, highly skilled technicians, and a range of raw materials.
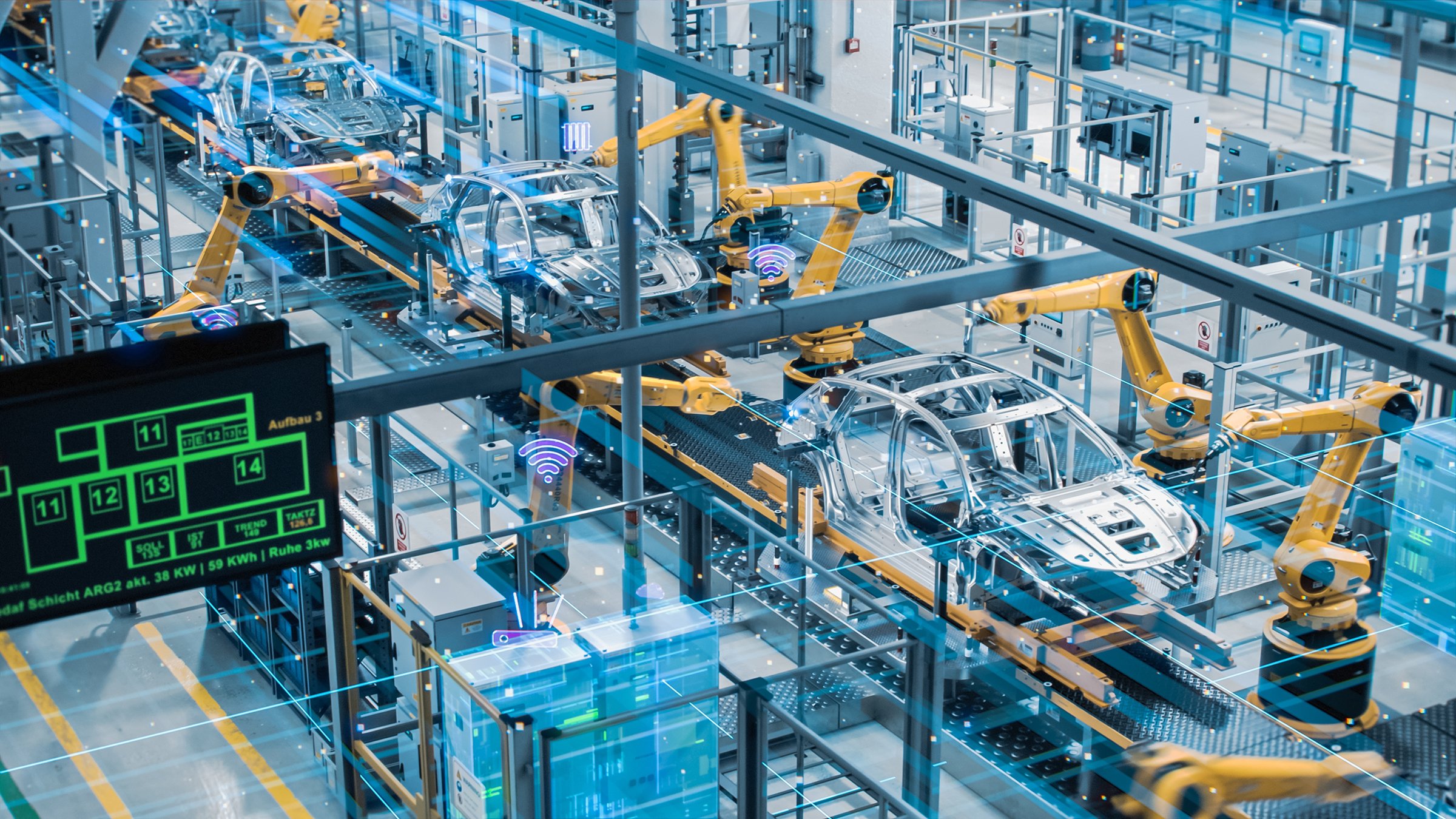

Applications of Automotive Automation
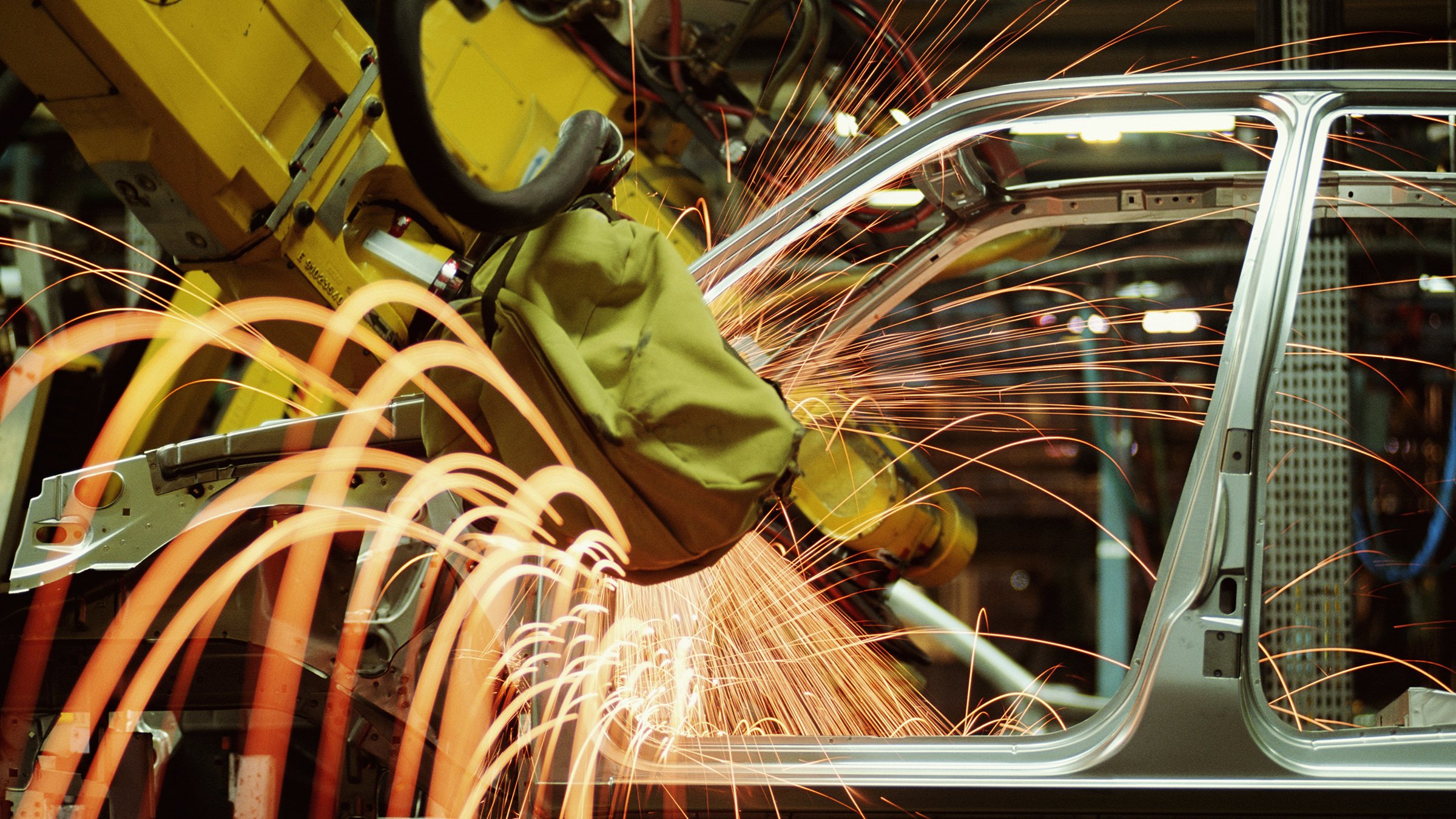
Common automotive manufacturing processes that can be enhanced with automation include welding, material handling, assembly, inspection, and testing. Here are just a few of the many ways automotive automation can power the manufacturing process.
- Assembly Systems – Automation can be incorporated into automotive assembly lines to perform tasks like riveting, fastening, or connecting parts. It can also handle tasks like glass installation, urethane application, and component bonding.
- Welding – Automated welding solutions empower automotive manufacturers to join materials together faster and safer than with traditional welding. Automated welding helps to improve weld quality, reduces waste, and keeps employees away from dangerous situations.
- Paint and Sealer Applications – Automated paint and sealer applications enable the safe and efficient applications of liquid materials such as paint and tire sealants.
- Glass Installation – Automotive manufacturers can incorporate automated dispensing and decking systems to improve quality, safety, and efficiency in glass applications and installations.
- Tire and Wheel Assembly – Automated tire and wheel systems can include automated weight application for wheel balancing, tire and wheel vision systems, and automated tire pressure monitoring systems.
These represent a small portion of what is achievable with automotive automation. Technology is advancing continuously, and more and more car manufacturing processes are being automated every day.
Challenges in Automotive Manufacturing
Because automotive manufacturers rely on a range of steps, processes, and specialized equipment, they often face a number of challenges that can prevent them from delivering products in a timely manner while adhering to the necessary regulations. Common challenges in automotive manufacturing include:
- Supply Chain Management
- Adjusting to Changing Market Conditions
- Ensuring Quality and Reliability Standards are Met
- Regulatory Compliance
- Cost Management
To help navigate these common automotive manufacturing challenges, many producers are opting for smart manufacturing technology, including automotive automation.
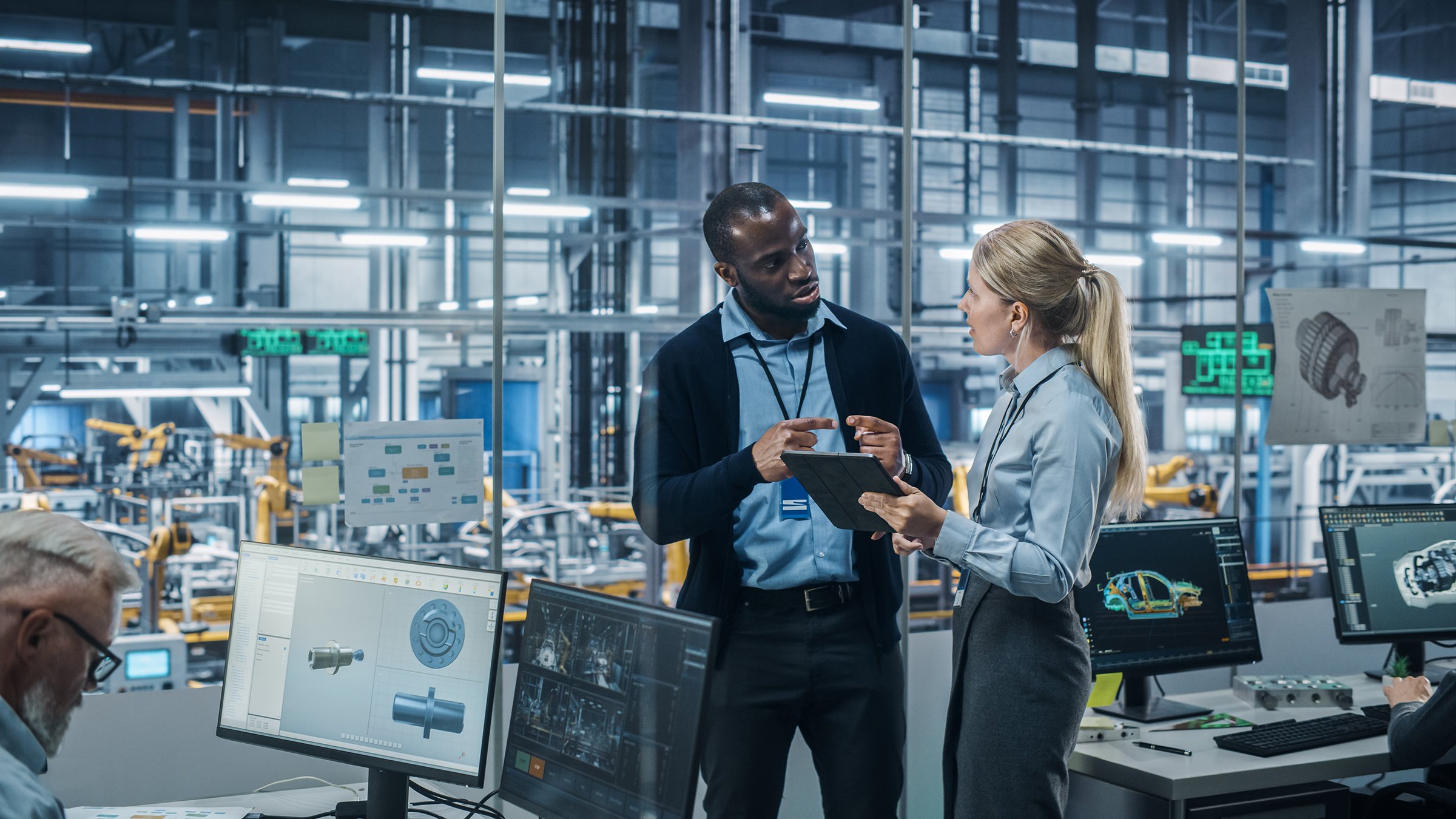

What is Automotive Robotics?
Automotive robotics is a subsection of automotive automation that refers specifically to the use of robotics to enhance the manufacturing of automobiles and their parts. As products and manufacturing processes develop, automotive robotics empower car manufacturers to stay flexible, adjust to meet shifting demands, and increase throughput and efficiency without sacrificing quality.
Robotics in Automotive Manufacturing
Common robotic technology used in automotive manufacturing includes:
- Welding Robots – Enable more efficient spot welding of car body panels and components.
- Robotic Assembly – Robotic arms in automotive manufacturing can perform tasks like screw driving, windshield installation, and wheel mounting, as well as small component assemblies.
- Automotive Machine Tending – Automated robots allow for the unloading of hot moldings from injection molding or die-casting machines, protecting human employees from performing dangerous tasks.
- Robotic Material Removal – Robots excel at performing complex tasks like trimming and cutting fabrics for headliners, trimming flash from plastic moldings, and polishing molds.
- Part Transfer Robots – Other dangerous jobs that are better suited for robotics include pouring molten metal in a foundry and transferring metal stamps from one press to the next. Robotic automation enables these processes to be carried out safely, without putting humans at risk.
Learn More About Automation in the Automotive Industry
Others also viewed
Based on your activity










