PID instruction timing diagrams
The following timing diagram examples describe execution scenarios for the PID instruction.
Successful PID execution
Successful PID execution
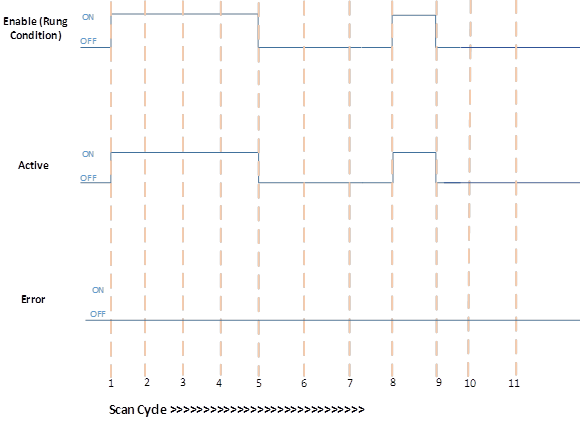
Scan Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
1, 8 | Rung condition becomes TRUE when:
|
2,3,4 | No change in Rung condition.
|
5, 9 | Rung condition becomes FALSE when:
|
6, 7, 10, 11 | No change in Rung condition.
|
PID execution with Error
PID execution with Error
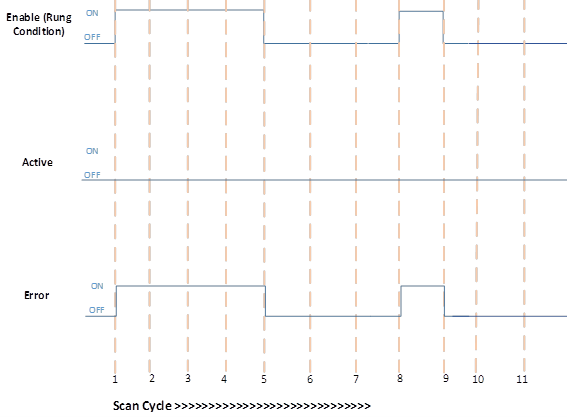
Scan Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
1, 8 | Rung condition becomes TRUE when:
|
2,3,4 | No change in Rung condition.
|
5, 9 | Rung condition becomes FALSE when:
|
6, 7, 10, 11 | No change in Rung condition.
|
PID execution with Error then successful execution
PID execution with Error then successful execution
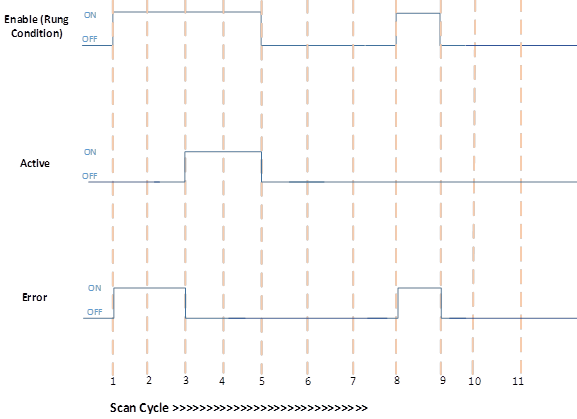
Scan Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
1, 8 | Rung condition becomes TRUE when:
|
2 | No change in Rung condition.
|
3, 4 | No change in Rung condition.
|
5, 9 | Rung condition becomes FALSE when:
|
6, 7, 10, 11 | No change in Rung condition.
|
Successful PID execution and Error
Successful PID execution and Error
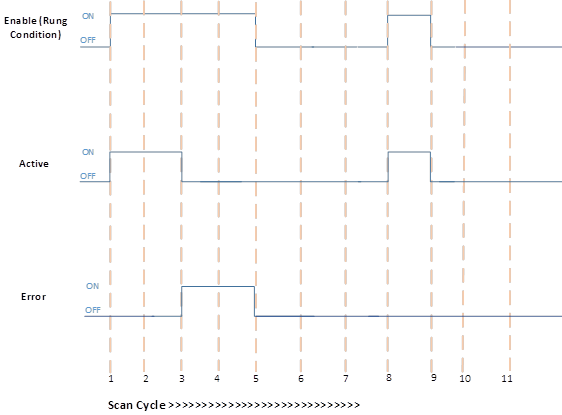
Scan Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
1, 8 | Rung condition becomes TRUE when:
|
2 | No change in Rung condition.
|
3, 4 | No change in Rung condition.
|
5, 9 | Rung condition becomes FALSE when:
|
6, 7, 10, 11 | No change in Rung condition.
|
Provide Feedback
