Array concepts
Arrays let you refer to a group of data (of the same data type) by the same name and to use a number (index) to identify an individual element. An element in an array can be a/an:
- Atomic data type
- Structure data type
You specify an element in an array by its subscript(s). Enter the array tag name followed by the subscript(s) in square brackets. The subscript(s) must specify a value for each dimension of the array. Dimensions are zero-based.
For this array | Specify |
|---|---|
one dimension | array_name[subscript_0] |
two one dimension | array_name[subscript_0, subscript_1] |
three dimension | array_name[subscript_0, subscript_1, subscript_2] |
An array can have as many as three dimensions. The total number of elements in an array is the product of each dimension’s size.
This array: | Stores this data: | Example: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
one dimension | 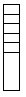 | Tag name | Type | Dimension 0 | Dimension1 | Dimension 2 |
one_d_array | DINT[7] | 7 | -- | -- | ||
total number of elements = 7 | ||||||
valid subscript range DINT[x] where x=0-6 | ||||||
two dimension | 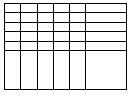 | Tag name | Type | Dimension 1 | Dimension 0 | Dimension |
two_d_arry | DINT[4,5] | 4 | 5 | -- | ||
total number of elements = 4 * 5 = 20 | ||||||
valid subscript range DINT[x,y] where x=0–3; y=0–4 | ||||||
three dimension | 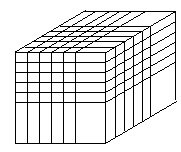 | Tag name | Type | Dimension 2 | Dimension 1 | Dimension 0 |
three_d_array | DINT[2,3,4] | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
total number of elements = 2 * 3 * 4 = 24 | ||||||
valid subscript range DINT[x,y,z] where x=0–1; y=0–2, z=0–3 | ||||||
Provide Feedback
