Name conventions and limitations
AADvance-Trusted SIS Workstation software®
has these name conventions and limitations:Projects | |
|---|---|
Project names | Project names have a maximum of 32 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a project name must be a letter or digit; project names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique for projects within a directory. |
Controller names | Controller names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a controller name must be a letter or digit; controller names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique for the same type of elements within a scope. |
Programs in a project | Projects can contain up to 65 536 programs. |
Hierarchical levels | Projects can have up to 65 536 levels. |
Program Organization Units (POUs) (Programs,
Functions, and Function Blocks) | |
POUs | Projects have up to 65 536 POUs. |
Program names | Program names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a program name must be a letter or digit; program names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique. |
Function names | Function names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a function name must be a letter or digit; function names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique. |
Operator parameters | The addition (+), multiplication (*), AND, and OR operators have a maximum of 127 input parameters. |
Function parameters | Functions have a maximum of 128 parameters (127 inputs and one output) |
Function parameter names | Function parameter names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a parameter name must be a letter or digit; parameter names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique for the same type of elements within a scope. |
Function block names | Function block names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a function block name must be a letter or digit; function block names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique. |
Function block parameters | Function blocks have a maximum of 128 parameters (inputs and outputs) |
Function block parameter names | Function block parameter names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a parameter name must be a letter or digit; parameter names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique for the same type of elements within a scope. |
Variables | |
Dictionary variables | The dictionary contains up to 4 294 967 296 entries for each variable type. |
Variable names | Variable names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a variable name must be a letter or digit; variable names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique for the same type of elements within a scope. |
BOOL variables | Boolean variables have the Boolean value TRUE (1) or FALSE (0). |
SINT variables | SINT variable integer values range from -128 to +127. Short integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
USINT variables | USINT variable integer values range from 0 to 255. Unsigned short integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
BYTE variables | BYTE variable integer values range from 0 to 255. BYTE constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
INT variables | INT variable integer values range from -32768 to +32767. Integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
UINT variables | UINT variable integer values range from 0 to 65535. Unsigned integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
WORD variables | WORD variable integer values range from 0 to 65535. WORD constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
DINT variables | DINT variable integer values range from -2147483648 to +2147483647. Double integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
UDINT variables | UDINT variable integer values range from 0 to 4294967295. Unsigned double integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
DWORD variables | DWORD variable integer values range from 0 to 4294967295. Double word constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
LINT variables | LINT variable integer values range from -9223372036854775808 to +9223372036854775807. Long integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
ULINT variables | ULINT variable integer values range from 0 to 18446744073709551615. Unsigned long integer constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
LWORD variables | LWORD variable integer values range from 0 to 18446744073709551615. Long word constants must begin with a prefix identifying the base. There is no prefix for DECIMAL values. For HEXADECIMAL values the prefix is "16#", for OCTAL values the prefix is "8#", and for BINARY values the prefix is "2#". |
REAL variables | Real variables have six significant digits. For larger values, the maximum possible value is 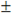 3.402823466E+38 while for smaller values, the minimum possible value is 3.402823466E+38 while for smaller values, the minimum possible value is 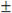 1.175494351E-38. Values greater than 1.175494351E-38. Values greater than 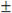 3.402823466E+38 and greater than 0.0 but less than 3.402823466E+38 and greater than 0.0 but less than 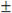 1.175494351E-38 are not supported. Write real literal values with either decimal or scientific representation. The exponent part of a real scientific expression must be a signed integer value ranging from -37 to +37. The scientific representation uses the 'E' letter to separate the mantissa part and the exponent. 1.175494351E-38 are not supported. Write real literal values with either decimal or scientific representation. The exponent part of a real scientific expression must be a signed integer value ranging from -37 to +37. The scientific representation uses the 'E' letter to separate the mantissa part and the exponent. |
LREAL variables | Long real variables have 15 significant digits. For larger values, the maximum possible value is 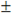 1.7976931348623158e+308 while for smaller values, the minimum possible value is 1.7976931348623158e+308 while for smaller values, the minimum possible value is 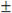 2.22507385850721E-308. Values greater than 2.22507385850721E-308. Values greater than 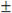 1.7976931348623158e+308 and greater than 0.0 but less than 1.7976931348623158e+308 and greater than 0.0 but less than 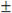 2.22507385850721E-308 are not supported. Write long real literal values with either decimal or scientific representation. The range of a real scientific expression must be a signed integer value from 1.7E -308 to 1.7E +308. 2.22507385850721E-308 are not supported. Write long real literal values with either decimal or scientific representation. The range of a real scientific expression must be a signed integer value from 1.7E -308 to 1.7E +308. |
TIME variables | Time variables can have positive values ranging from 0 to 49d17h2m47s294ms. The time literal value must begin with the "T#" or "TIME#" prefix. |
DATE variables | Date variable values range from 1970-01-01 to 2038-01-18. The date literal expression must begin with the "D#" or "DATE#" prefix. |
STRING variables | STRING variable string capacity has a maximum of 255 characters excluding the terminating null character (0), a byte for the current length of the string, and a byte for the maximum length of the string. String variables can contain any character of the standard ASCII table. Characters must be preceded and followed by single quote (') characters. When placing single quote (‘) characters within a string literal, these characters must be preceded by the dollar ($) character. |
Alias names | Alias names have a maximum of 128 characters consisting of letters, digits, and these special characters: !, #, $, %, &, \, *, +, -, /, <, :, =, >, ?, @, ^, _, `, |, and ~. |
User-defined Types | |
Array names | Array names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for an array name must be a letter or digit; array names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique. |
Structure names | Structure names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a structure name must be a letter or digit; structure names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique. |
Defined Words | |
Defined word names | Defined word names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for a defined word name must be a letter or digit; defined word names cannot end with an underscore character. Do not use reserved words, defined words, or data types (elementary, structures, or arrays) for names. Names must be unique for the same type of elements within a scope. |
Defined word equivalents | Defined word equivalents have a maximum of 128 characters. |
Sequential Function Chart (SFC) | |
SFC steps per program | SFC programs have a maximum of 65 536 steps. |
SFC transitions per program | SFC programs have a maximum of 65 536 transitions. |
SFC step and transition names | SFC step and transition names have a maximum of 128 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores. The last character for an SFC step and transition name must be a letter or digit; SFC step and transition names cannot end with an underscore character. SFC step and transition names cannot contain reserved keywords or share the same names as the variables. |
Provide Feedback
