Functions
Functions are program organization units (POUs) that have one or more input parameters and one output parameter. Programs, functions, or function blocks call functions. A function has no instance and does not store local data. Local data is generally lost from one call to the other.
The parent program drives the execution of the function. The execution of the parent program is suspended until the function ends:
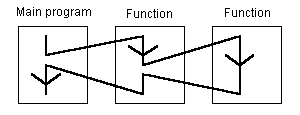
Any POU of any section calls one or more functions. A function has local variables.
Recursivity is not supported during function calls. A build error occurs when a function of the
Functions
section calls itself or one of its called functions. Functions do not store the local values of local variables. Since functions do not instantiate, functions cannot call function blocks.Define the interface of a function with a type and a unique name for each input parameters or output parameter. Functions have up to 31 input parameters and one output parameter.
- Unique names limited to eight characters and must begin with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores.
- A maximum of 32 parameters -- 31 inputs and one output with names limited to 32 characters beginning with a letter or single underscore followed by letters, digits, and single underscores.
- Names cannot be reserved words, defined words, or data types.
Provide Feedback
