Configure a Modbus Slave
Modbus
SlaveConfigure up to 10
Modbus®
slaves to operate in the T8151 Communications Interface
. Allocate these slaves to serial or Ethernet ports.Since a
Trusted®
system that is Modbus
slave has no control over the messages received from the master, the system can have longer than expected delays between messages. Allocate more time for communications processing between the T8151 Communications Interface
and the processor by specifying a sleep period between scans in the Trusted
system configuration. To set a sleep period between scans, in the T8110
configuration, set the sleep period to approximately 32 ms longer than the current scan time from the Trusted
TMR ProcessorToolset Debugger
window. This longer sleep period provides time on most scans for communications tasks and evens out the scan time. It also lengthens the scan time while ensuring that process safety times are not compromised and the maximum scan time and I/O module watchdog times are adjusted proportionately to the change in average scan time.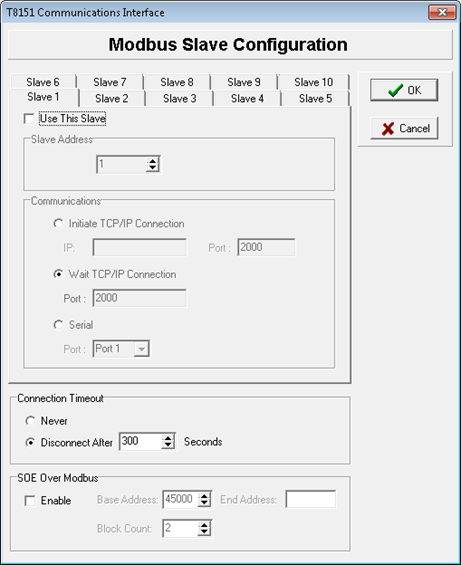
When configuring a
Modbus
slave, define these properties:Property | Description |
|---|---|
Slave Address | Slave address for communication with the T8151 Communications Interface . The address is usually 1 on a point-to-point link in the range 1 to 127. |
Communications | The type of connection between the Modbus slave and the Modbus master:
|
Connection Timeout | The time delay to allow Ethernet-based slaves to recover after a lost connection. This property should remain at the default value to disconnect after 300 seconds. This time delay is appropriate for communications where cable breaks are not normally expected, for example, not involving a modem or other link likely to disconnect. The TCP/IP stack does not detect the loss of Modbus communications caused by a pulled connection or cable break. The TCP/IP stack does not detect a broken connection and retains it as a valid connection. When the broken connection is recovered, the Modbus Master may resume communications using the existing connection but is more likely to establish a new connection. Each re-connection consumes one of the available connections. If re-connections occur on a regular basis, all available connections are consumed and connections are no longer possible. On early communications interfaces that do not recognize the connection timeout setting, removing and reinserting the communications interface and rebooting recovers the available connections. |
SOE Over Modbus | The protocol that allows buffered transfer of events via a T8151 Communications Interface Modbus slave. This protocol provides access to the SOE buffer events, not Process Historian, over a Modbus data link where the default OPC server/SOE collector protocols prove too slow. However, the SOE Over protocol requires an application in the Modbus Modbus master remote end to read, interact with and interpret the buffer, and assign event data to variables. For more information on events and their configuration, see Product Description PD-8013, Trusted SOE and Process Historian Package. For more information on the SOE Over protocol and data block format, see Product Description PD-T8151B, Modbus Trusted Communication Interface.SOE Over is implemented as a service running on a Modbus T8151 Communications Interface . When enabled, the service manages a window of Modbus addresses that implement the protocol which is automatically available on all ports of that module that are configured as Modbus slaves.The settings in the Modbus Slave ConfigurationSOE Over Modbus Requirements:
|
To configure a
Modbus
slave- In theT8151 Communications Interface, clickConfigure.ModbusSlave
- In thewindow, select the slave number and define the properties.ModbusSlave Configuration
- Select theUse this Slavecheck box and indicate the slave address.
- Select the connection method for the slave:
- Initiate TCP/IP Connection. Indicate the TCP/IP address and port of theModbusmaster.
- Wait TCP/IP Connection. Indicate the port of the incoming connection.
- Serial port. Indicate one of four possible serial ports.
- Select a connection timeout:
- Never, where the Ethernet connection never times out
- Disconnect after, where the Ethernet connection times out after the indicated number of seconds. This property should remain at the default value to disconnect after 300 seconds.
- Use theSOE overservice:Modbus
- Select theEnablecheck box.
- Indicate these properties:
- Base Address, starting address of the window used by the protocol
- End Address, last address of theModbusaddress window used by the protocol
- Block Count, number of events that theModbusmaster can read in a singleModbusread
- ClickOK.
Provide Feedback
