Applying best practices
Use these best practices for keeping program organization unit (POU) code simple and clear.
Best Practice | Example |
|---|---|
Avoid loops in networks. In Function Block Diagram (FBD), loops can yield Compiler Verification Tool (CVT) mismatches due to the execution order. The compiled execution is not at fault, only the CVT comparison. Use variables to avoid mismatches. | FBD network with a loop: 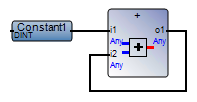 Best practice: 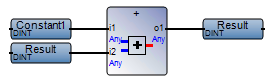 |
Use simple networks. In FBD, a circular pattern causing issues occurs when the output of a function block is linked as the input of two or more function blocks. | FBD network with a circular pattern: 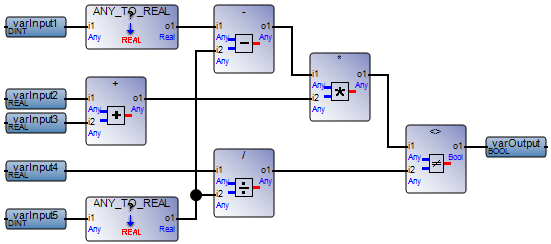 Best practice: 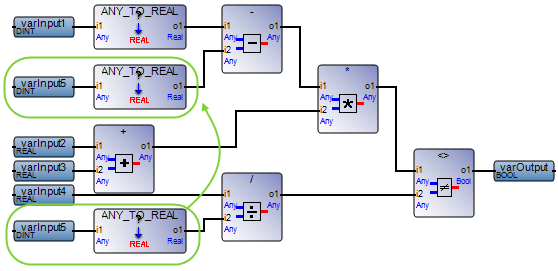 |
Avoid overlapping networks. In FBD, separate networks from one another to avoid network overlapping. | FBD program with overlapping networks: 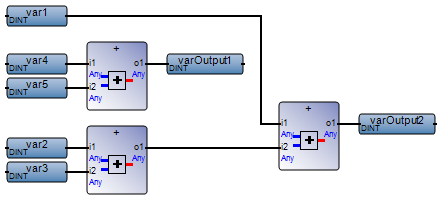 Best practice: 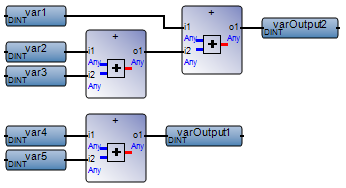 |
Place labels outside of FBD networks | Label placed inside an FBD network: 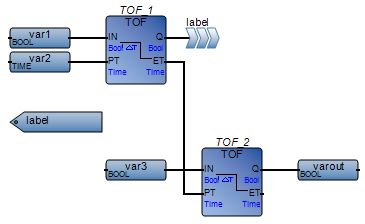 Best practice: 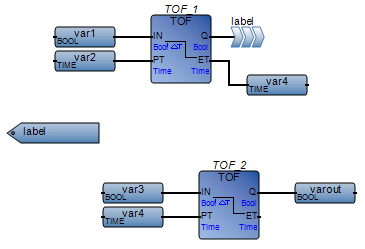 |
Avoid using constants as inputs for operators. In FBD, insert a temporary variable between the constant and the operator when using constants as inputs for an operator. | FBD network with constants as inputs: 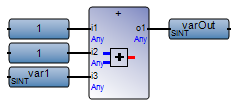 Best practice: 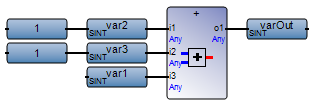 |
Avoid using user-defined function blocks with no input or output parameters. Define at least one input to each user-defined function block. This avoids CVT errors and for the correct execution. | FBD program with a user-defined function block with no input or output parameters: 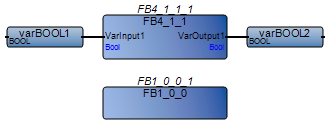 Best practice: 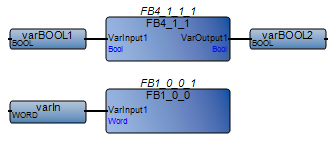 |
Avoid using vertical bars in FBD POUs. Vertical bars in FBD can yield CVT mismatches due to the execution order. Create a user-defined Ladder Diagram (LD) POU and then use the block in the required FBD application. | FBD program using vertical bars: 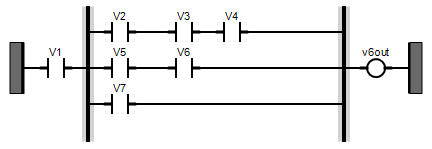 xxx := V1; v6out := (((xxx & V5) & V6) OR (xxx & V7) OR (((xxx & V2) & V3) & V4)); Best practice: 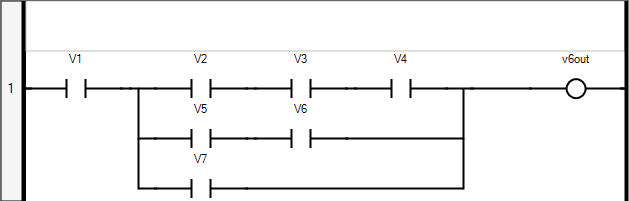 Then use the user-defined LD POU in the required FBD application. |
Avoid assigning multiple levels of variables in a network. Flatten variables on a single level to avoid CVT mismatches due to the execution order. | FBD network with multiple levels of variables:  Best practice: 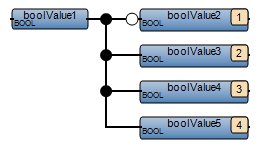 |
Update each instance of a function or function block after adding, removing, reordering, renaming, changing data type, or changing direction. Identify all POUs using the modified instances of the function or function block with the Cross Reference Browser , then open each POU and reselect the modified instance using the Block Selector . | Example based on reordering the input parameters of a function from the Parameters View . The actual function instance in the POU is not updated to the current or expected input order definition.Actual: Funct1 function in the Parameters View :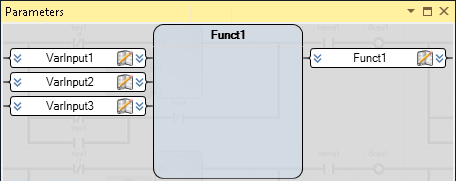 Funct1 function in POU without reselecting the instance: 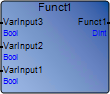 Expected: Funct1 function in the Parameters View : Funct1 function in POU after reselecting the instance 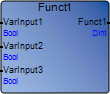 |
Avoid using power rails with negated connections. Use variables providing the required input value to avoid CVT errors. | Using a power rail with negated connections: 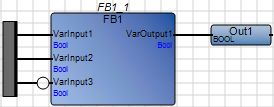 Best practice: 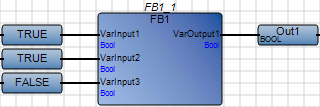 |
In Structured Text (ST), avoid using the result of an operation as a parameter to a function. Store the result of the operation in a temporary variable to prevent safety issues. | ST statement containing the result of an operation as a parameter to a function: dVal := TON_BOOL((realMin > realMax), boolValue); Best practice: boolParam := (realMin > realMax); dVal := TON_BOOL(boolParam, boolValue); |
FBD programs are executed from top to bottom. Avoid separate segments of a FBD program on the same line. | Situation to avoid: 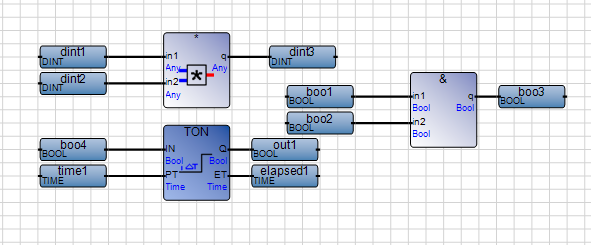 Best practice 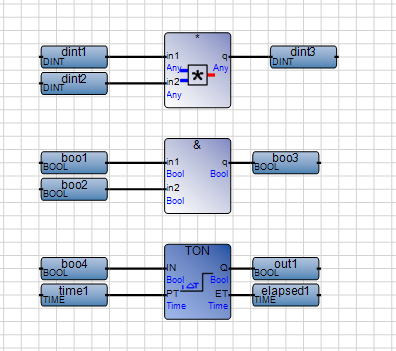 |
Provide Feedback
