for_do
Use the for_do loop to perform an action a number of times before doing anything else.
When enabled, the
for
instruction repeatedly executes the Routine until the Index
value exceeds the Terminal value. The step value can be positive or negative. If it is
negative, the loop ends when the index is less than the terminal value. If it is positive,
the loop ends when the index is greater than the terminal value.Each time the
for
instruction executes the routine, it adds the Step size to the
Index.Do not loop too many times in a single scan. An excessive number of repetitions causes the controller watchdog to timeout and causes a major fault.
Operands
for count:= initial_value to
final_value by increment do
<statement>;
end_for;
Operand | Type | Format | Description |
count | SINT INT DINT | Tag | Tag to store count position as the for_do executes |
initial_ value | SINT INT DINT | Tag expression Immediate | Must evaluate to a number Specifies initial value for count |
final_ value | SINT INT DINT | Tag expression Immediate | Specifies final value for count, which determines when to exit the loop |
increment | SINT INT DINT | Tag expression Immediate | (Optional) amount to increment count each time through the loop If you don’t specify an increment, the count increments by 1. |
IMPORTANT:
- Do not iterate within the loop too many times in a single scan.
- The controller does not execute other statements in the routine until it completes the loop.
- A major fault occurs when completing the loop takes longer than the watchdog timer for the task.
- Consider using a different construct, such as if_then.
Description
The syntax is described in the table.
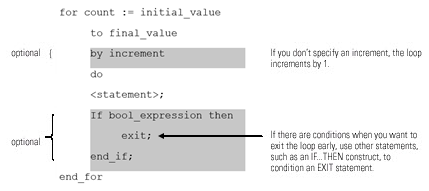
This diagrams illustrates how a for_do loop executes, and how an exit statement leaves the
loop early.
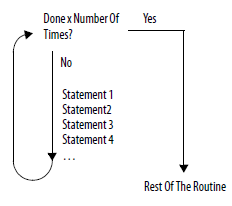 | 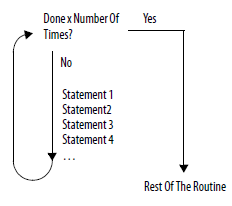 |
The for_do loop executes a specific number of times. | To stop the loop before the count reaches the last value, use an exit
statement. |
Affects Math Status Flags
No
Major/Minor Faults
A major fault will occur if | Fault type | Fault code |
The construct loops too long. | 6 | 1 |
Example 1
If performing the following, | Enter this structured text |
Clear bits 0…31 in an array of BOOLs: Initialize the subscript tag to 0. Clear i . For example, when subscript = 5, clear array[5]. Add 1 to subscript. If subscript is ≤ to 31, repeat 2 and 3. Otherwise, stop. | For subscript:=0 to 31 by 1 do |
array[subscript] := 0; | |
End_for; |
Provide Feedback
