Advanced Time Sync
The Advanced Time Sync dialog displays information that is related to
CIP Sync™
time synchronization. The information appears only if the project is online and Time Synchronization is enabled on the Date/Time tab.
IMPORTANT:
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Software
- Access to software that manages PTP on a control system network must be limited to users who are trained on the administration of industrial control system time including PTP. This includes the PTP update tool that is supplied by Rockwell Automation, or other publicly available PTP management software. Incorrect updates while a control system is running can disrupt the operation of the control system, including major faults and some devices taken offline.
- When disabling PTP on a controller, to give the controller time to process the disable, use a two-second delay before setting the WallClockTime (WCT) in the controller. Otherwise, there is a risk of the Grandmaster clock overwriting the WCT.
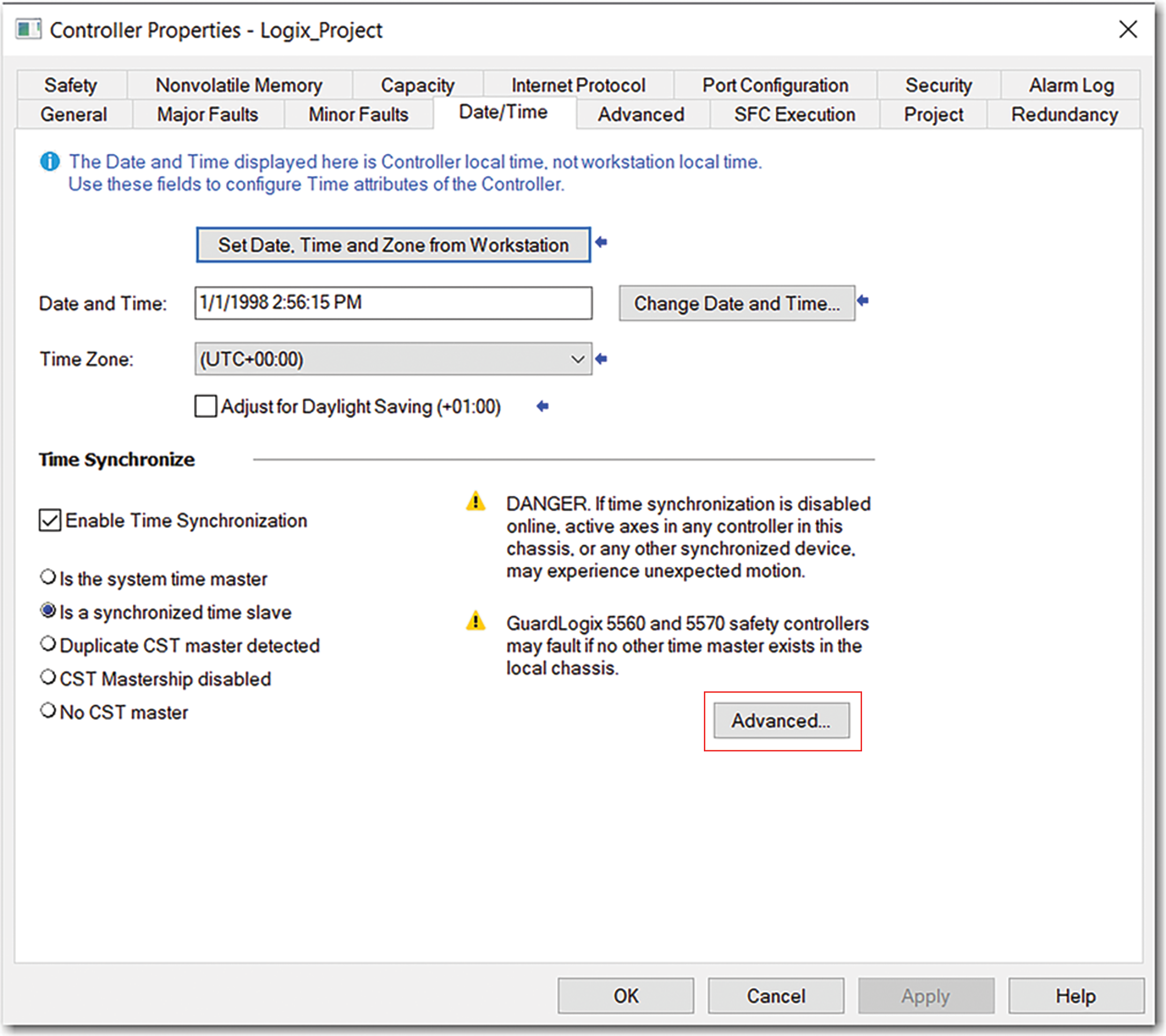
On the Date/Time tab, click the Advanced button.
Controller Properties Date/Time Tab
The Advanced Time Sync dialog box opens.
Advanced Time Sync
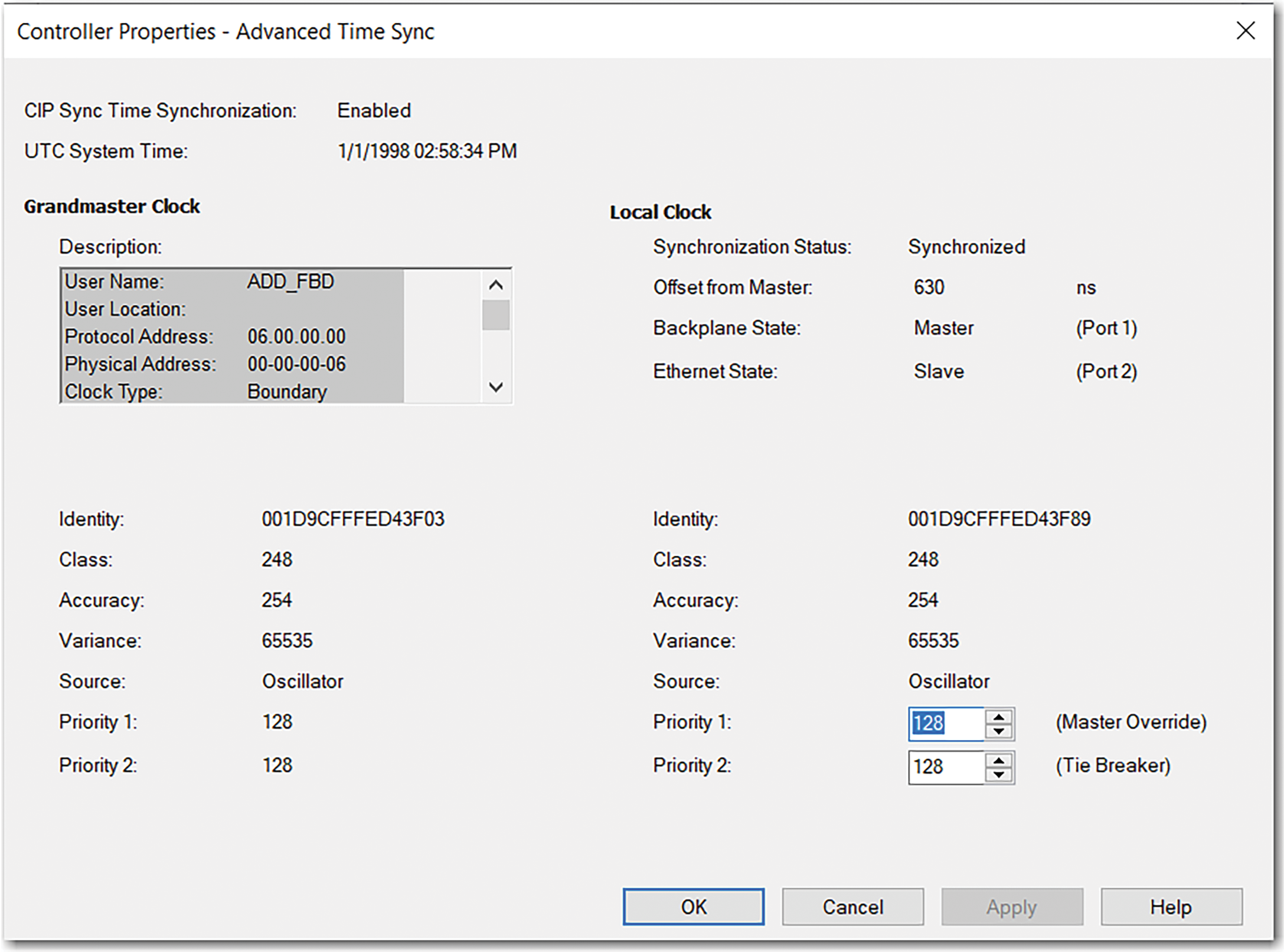
Grandmaster Clock | |
|---|---|
Description | Displays information about the Grandmaster clock. The vendor of the Grandmaster device controls this information. The following information is specified:
Use the vertical scroll bar to view the data. |
Identity | Displays the unique identifier for the Grandmaster clock. The format depends on the network protocol. Ethernet network encodes the MAC address into the identifier. |
Class | Displays a measure of the quality of the Grandmaster clock. Values are defined from 0…255 with zero as the best clock. |
Accuracy | Indicates the expected absolute accuracy of the Grandmaster clock relative to the PTP epoch. The accuracy is specified as a graduated scale that starts at 25 nsec and ends at greater than 10 seconds or unknown. The lower the accuracy value, the better the clock. |
Variance | Displays the measure of inherent stability properties of the Grandmaster clock. The value is represented in offset scaled log units. The lower the variance, the better the clock. |
Source | Displays the time source of the Grandmaster clock. The available values are:
|
Priority 1 / Priority 2 | Displays the relative priority of the Grandmaster clock to other clocks in the system. The priority values range from 0…255. The highest priority is zero. The default value for both settings is 128. |
Local Clock | |
Synchronization Status | Displays whether the local clock is synchronized or not synchronized with the Grandmaster reference clock. A clock is synchronized if it has one port in the slave state and is receiving updates from the master. |
Offset to Master | Displays the amount of deviation between the local clock and the Grandmaster clock in nanoseconds. |
Backplane State | Displays the current state of the backplane. The available values are: Initializing, Faulty, Disabled, Listening, PreMaster, Master, Passive, Uncalibration, Slave, or None. |
Ethernet State | Displays the state of the Ethernet port. The available values are: Initializing, Faulty, Disabled, Listening, PreMaster, Master, Passive, Uncalibration, Slave, or None. |
Identity | Displays the unique identifier for the local clock. The format depends on the network protocol. Ethernet network encodes the MAC address into the identifier. |
Class | Displays a measure of the quality of the local clock. Values are defined from 0…255, with zero as the best clock. |
Accuracy | Indicates the expected absolute accuracy of the local clock relative to the PTP epoch. The accuracy is specified as a graduated scale that starts at 25 nsec and ends at greater than 10 seconds or unknown. The lower the accuracy value, the better the clock. |
Variance | Displays the measure of inherent stability properties of the local clock. The value is represented in offset scaled log units. The lower the variance, the better the clock. |
Source | Displays the time source of the local clock. The available values are:
|
Provide Feedback
