Call functions
The structured text programming language can call functions. Function calls can be used in any expressions, and contain properties explained in the following table.
Function call properties
A function is an instruction block that has input parameters and one output parameter. It can be written in structured text (ST), ladder diagram (LD), or function block diagram (FBD) languages.
Property | Description |
|---|---|
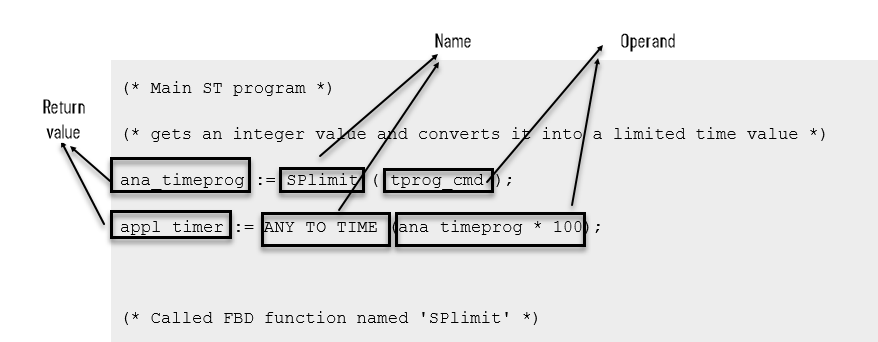
Name | The name of the called function written in an IEC 61131-3 language. |
Meaning | Calls an ST, LD, or FBD function, and gets its return value. |
Syntax | <variable> := <funct> (<par1>, ... <parN>); |
Operands | The type of return value and calling parameters must follow the interface defined for the function. |
Return value | Value returned by the function. |
Function call example
When setting the value of the return parameter in the body of a function, you can assign the return parameter using the same name as the function:
FunctionName := <expression>;
Example: IEC 61131-3 function call
(* Main ST program *) (* gets an integer value and converts it into a limited time value * appl_timer := ANY_TO_TIME (ana_timeprog * 100); (* Called FBD function named 'SPlimit' *)
Provide Feedback
