Determine Controller Memory Information
This is information is not applicable to
CompactLogix
5380, ControlLogix
5580 and 5590, Compact GuardLogix
5380, GuardLogix
5580, and ControlLogix 5590 controllers. In these
controllers, the memory used attributes are not supported or accessible.The memory of the controller is divided into I/O memory and expansion memory. This table
shows how the controller uses each type of memory:
This | Uses memory from |
|---|---|
I/O tags | I/O memory |
produced tags | |
consumed tags | |
communication via MSG instructions | |
communication with workstations | |
tags other than I/O, produced, or consumed tags | expansion memory |
logic routines | |
communication with polled (OPC/DDE) tags that use FactoryTalk
Linx . | I/O memory and expansion memory |
Note that the controller returns values in the number of 32-bit words. To see a value in
bytes, simply multiply by 4.Use this procedure to get the following information about the
controller's memory:
- available (free) I/O and expansion memory
- total I/O and expansion memory
- largest contiguous block of I/O and expansion memory
Get Memory Information From the Controller
To get memory information from the controller, execute a Message (MSG) instruction that is
configured as follows:
From the Message Properties dialog - Configuration tab:
From the Message Properties dialog - Communication tab:

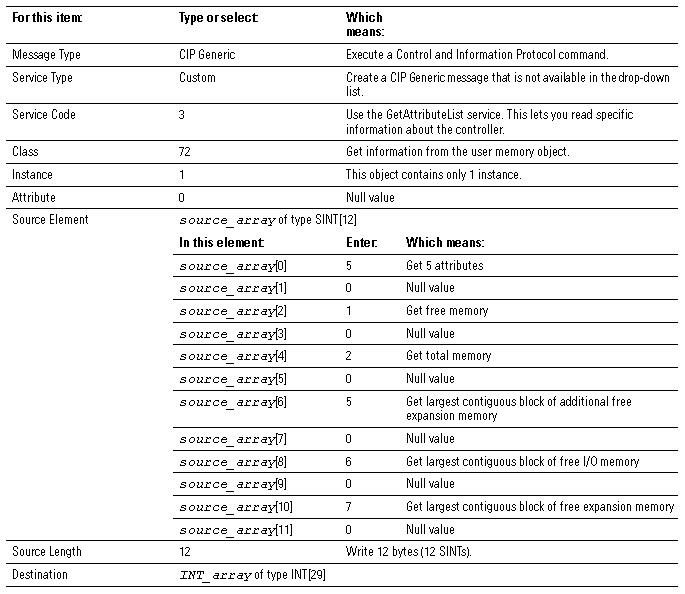
Choose the Memory Information You Want
The MSG instruction returns the following information to INT_array (the destination tag of
the MSG instruction).
IMPORTANT:
For a 1756-L55M16
controller, the MSG instruction returns two values for each expansion memory category. To
determine the free or total expansion memory of a 1756-L55M16 controller, add both values
for the category.
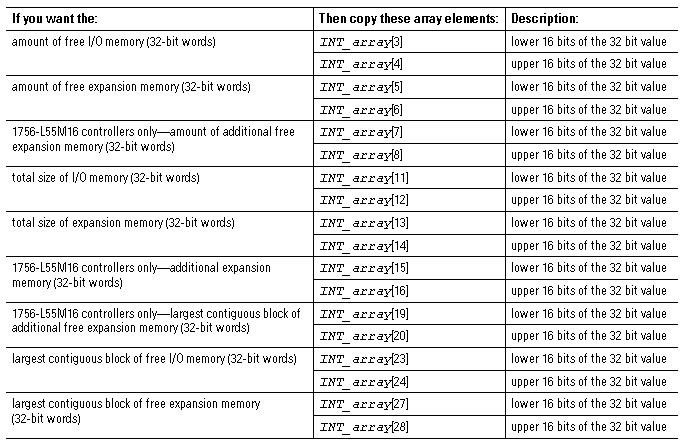
Convert INTs to a DINT
The MSG instruction returns each memory value as two separate INTs.
- The first INT represents the lower 16 bits of the value.
- The second INT represents the upper 16 bits of the value.
To convert the separate INTs into one usable value, use a Copy (COP) instruction, where:
In this operand: | Specify: | Which means: |
|---|---|---|
Source | first INT of the 2 element pair (lower 16 bits) | Start with the lower 16 bits |
Destination | DINT tag in which to store the 32-bit value | Copy the value to the DINT tag |
Length | 1 | Copy 1 times the number of bytes in the Destination data type. In this case, the
instruction copies 4 bytes (32 bits), which combines the lower and upper 16 bits
into one 32-bit value. |
Provide Feedback
