Safety Task
A safety application includes a safety task with a safety program and main routine.
Safety Task in Controller Organizer | Safety Program in Logical Organizer |
|---|---|
A safety task has these characteristics:
- The safety task is a periodic timed task. A periodic task is triggered at repetitive intervals. When triggered, the period task and its programs are executed. Data and outputs that the programs in the task establish retain their values until the next execution of the task or until another task manipulates them. Periodic tasks always interrupt the continuous task.
- The safety task cannot be deleted.
- Within the safety task, you can use multiple safety programs that are composed of multiple safety routines.
- You cannot execute standard routines from within the safety task.
- There can be only one safety task for a controller.
- You must configure the period and the priority of the safety task. The safety task can be interrupted according to the same rules as standard tasks, such as interruptions by the motion task. The motion task is always a higher priority than any user task.
IMPORTANT:
Large amounts of mapped safety tags or large amounts of safety produce/consume tag data can cause fluctuations in the safety task scan time of the controller.
IMPORTANT:
If the controller is configured for SIL 2 and the next slot to the right is empty or populated by a non-safety module, execution of the safety task can be delayed during powerup by five seconds or more.
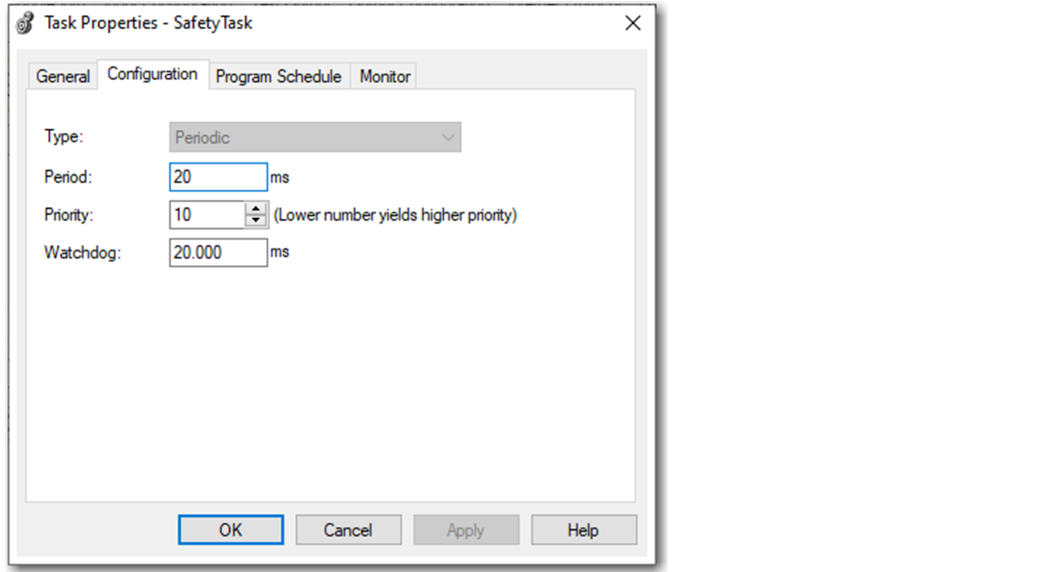
Safety Task Parameters
You can configure the following safety task parameters:
- Period—The safety task period is the time interval between successive executions of the safety task. The safety task period directly affects system reaction time. You cannot edit the safety task period online.
- Priority—Configure the safety task with a higher priority (lower number) to reduce fluctuations in execution time. A higher priority can allow a lower setting for the safety task watchdog, which improves the reaction time of the safety system.
- Watchdog—The safety task watchdog is the maximum time that is allowed from the start of the safety task to its completion.If a safety task watchdog timeout occurs, a nonrecoverable safety fault is generated in the controller.
To configure the safety task, right-click the safety task and choose Properties.
IMPORTANT:
The values that you define for the safety task parameters must meet the requirements that are defined in the following table.
Safety Task Parameters
Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
Period | Be sure that the safety task has enough time to execute its logic before it restarts. Enter a value of 2…500 ms. |
Priority | To get the most consistent safety task execution time and to minimize safety task watchdog faults, we recommend that you enter a value of 1 to make the safety task the highest priority user task. |
Watchdog | Enter a value of 2…500 ms. |
Safety Task Execution Details
The safety task executes like standard periodic tasks with these exceptions:
- Safety input tags and safety-consumed tags are updated only at the beginning of safety task execution. This process means that even though the I/O RPI can be faster than the safety task period, the data in the Safety Input tag only updates once at the beginning of each safety task execution. Safety input and consumed packets that arrive after the start of the safety task are buffered until the next execution of the safety task.
- Time is frozen at the start of safety task execution. As a result, timer-related instructions, such as TON and TOF, are not updated during a safety-task execution. They keep accurate time from one task execution to another, but the accumulated time is not changed during safety task execution.IMPORTANT: This behavior differs from standard Logix task execution.
- For standard tags that are mapped to safety tags, the standard tag values are copied to the safety tags at the start of the safety task:
- The standard tag is free to continue changing.
- Programming logic can change the safety tag within the safety task, but the change is not reflected back to the standard tag.
IMPORTANT: The addition of more mapped tags can increase the scan time. - Safety output tag values can be changed during the safety task scan by the safety programming logic. The final value is transmitted to safety modules at the end of the safety task scan.Likewise, safety produced values are transmitted to consuming safety controllers at the end of the safety task scan.
IMPORTANT:
While safety-unlocked and without a safety signature, the controller helps prevent simultaneous write access to safety memory from the safety task and communication commands. As a result, the safety task can be held off until a communication update completes. The time that is required for the update varies by tag size. Insufficient time can result in safety connection and safety watchdog timeouts.
To compensate for the hold-off time due to a communication update, you must increase the safety watchdog time.
Depending on the edit, a watchdog timeout can occur if there is insufficient time to complete the safety task operation.
When the controller is safety-locked or a safety signature exists, the scenarios that are described in this note cannot occur.
Provide Feedback
